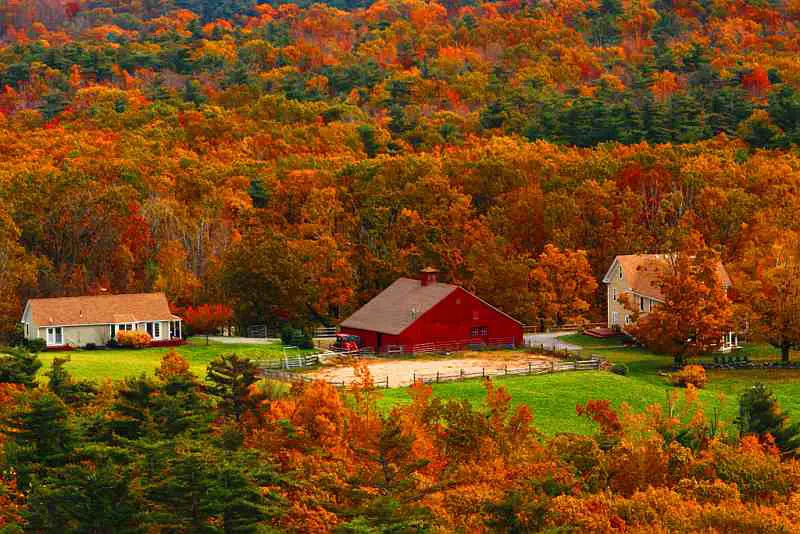
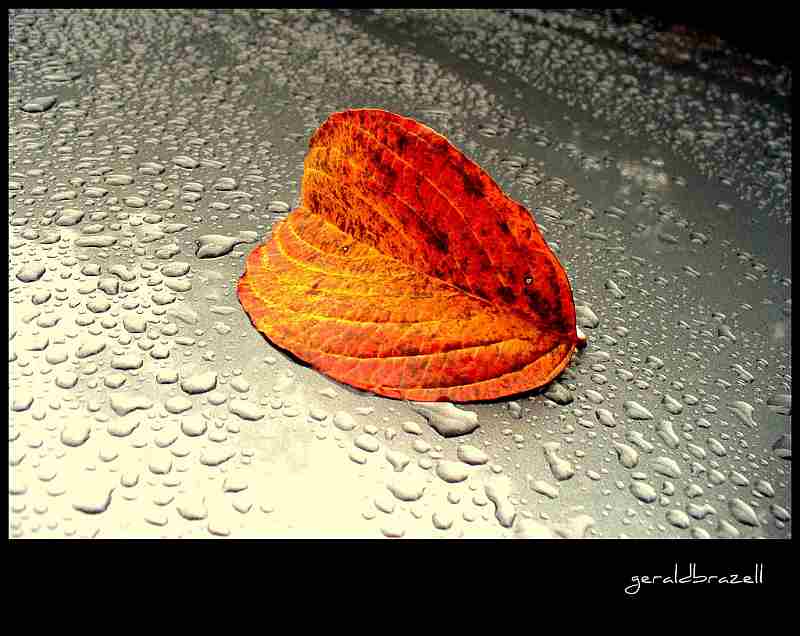
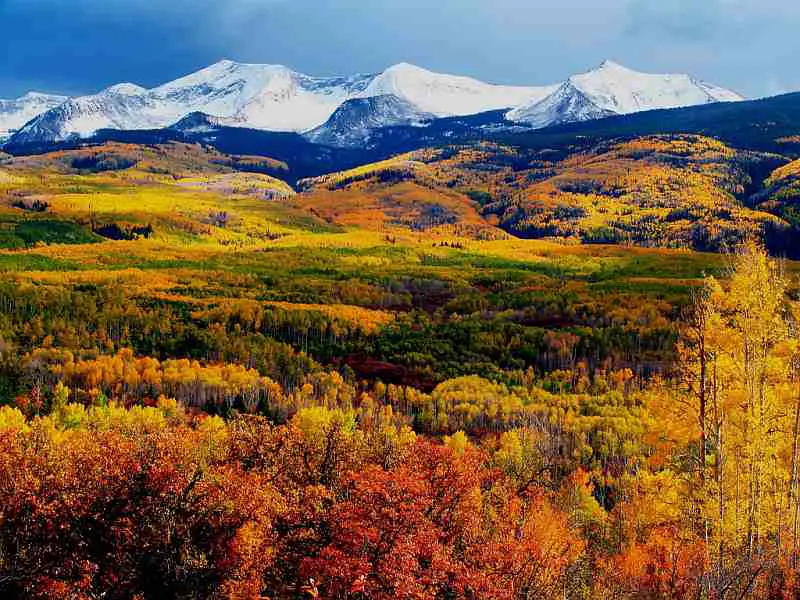
Fall is a beautiful time of year when the leaves on the trees change from their usual green to shades of yellow, red, orange and brown. What causes this and how do trees survive without leaves?
- Fall colors, and their duration, depend on factors such as temperature, water supply, and light.
- Leaves change colors because the veins that carry liquids throughout the leaf close off slowly as cork cells form at the base of every leaf. When this happens, there are fewer minerals and less water in the leaves. The chlorophyll ,which give leaves their green color, decreases.
- If it is rainy or overcast in the fall, colors will become more intense.
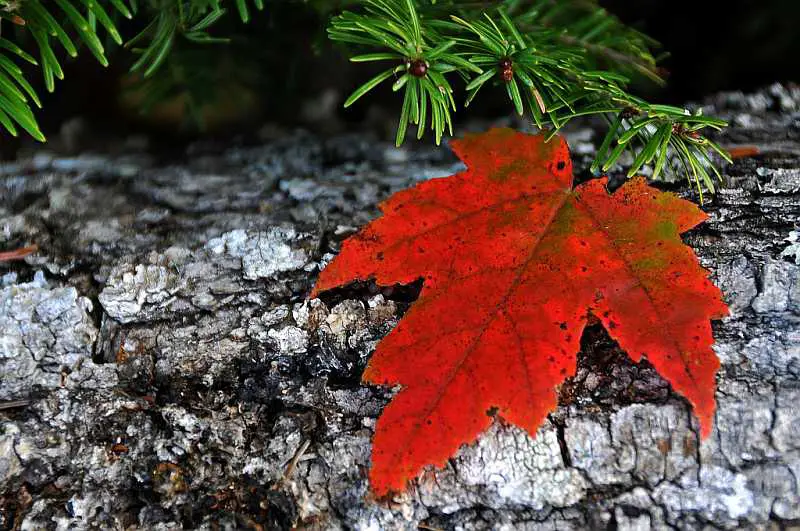
- Low temperatures–which are still not at freezing temperature–will often cause maple leaves to have a bright red fall color.
- Unlike most trees, conifers–which include pines, firs and many more–are evergreen. This means they do not change color or drop their leaves. Individual leaves can stay on a conifer for two to four or even more years.
- In the areas where winters are not very harsh, there are species of broad leaf trees which will not change color or drop their leaves.
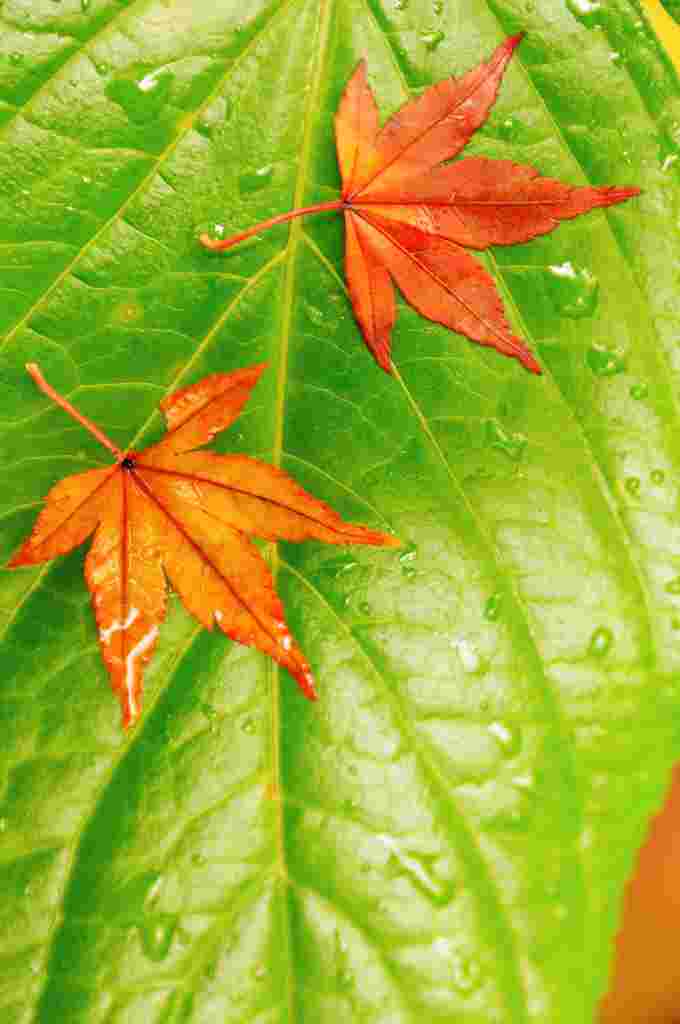
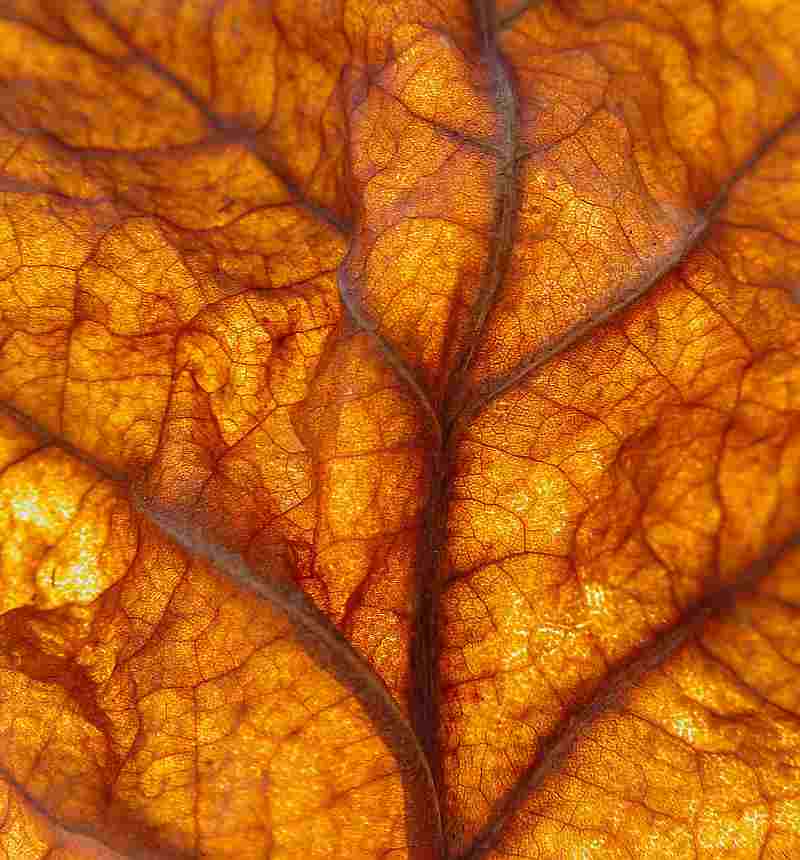
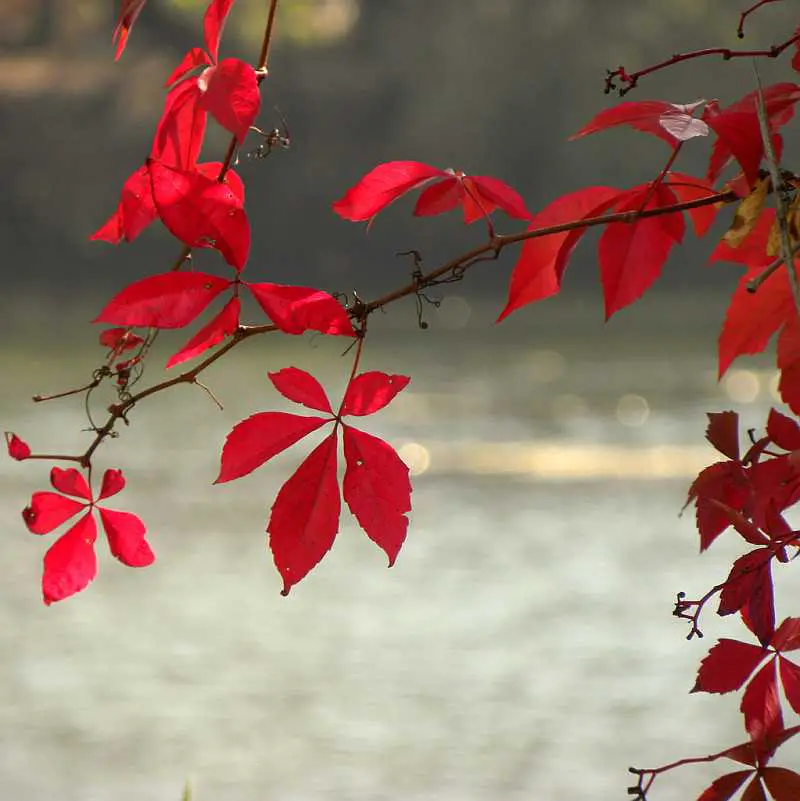
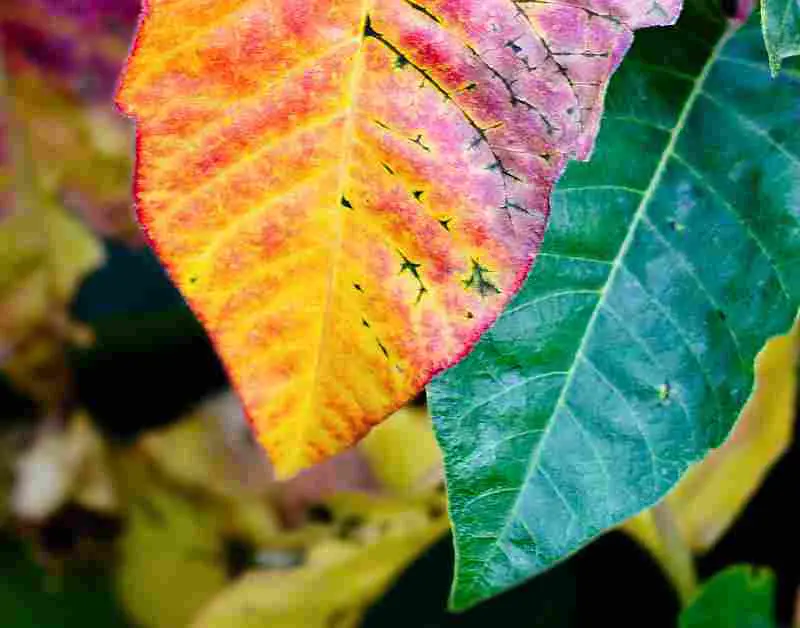
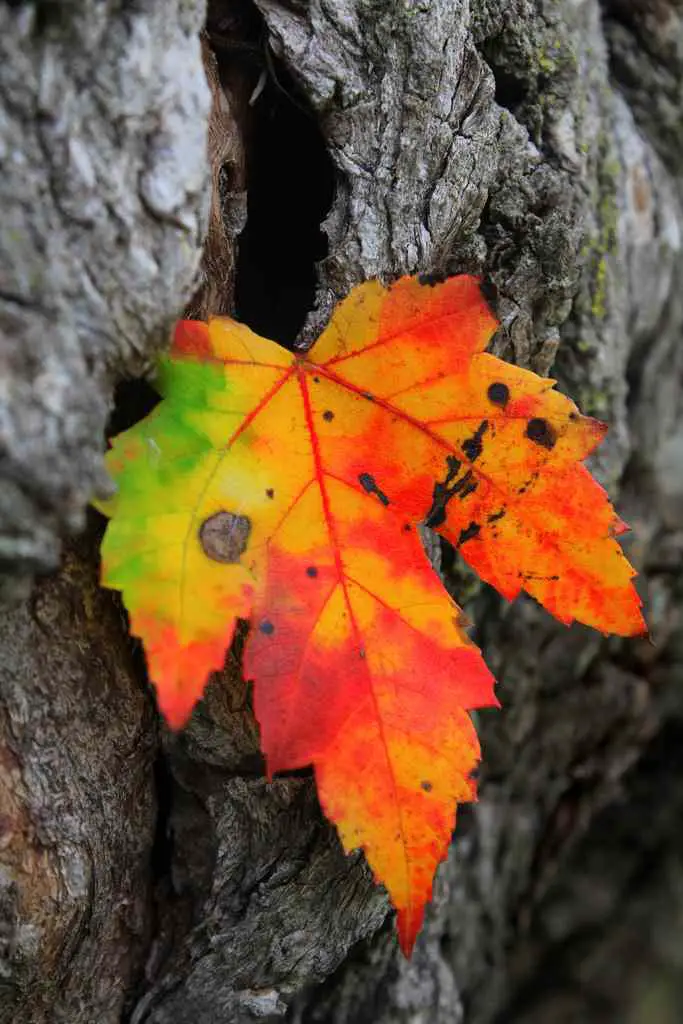
- Chlorophyll gives plants their green color while the yellows are created by xanthophyll. Oranges are created by carotenoids. And the anthocyanin in leaves add the color red to plants, but not all trees can produce it.
- When autumn colors occur, leaves do not actually lose their natural color. They return to their normal colors because chlorophyll is produced in the summer, which changes the leaves into the green color they normally are.
- When the leaves reach their complete brown color, they are dead because they are no longer receiving nutrients and minerals from the tree. The tree needs to save these nutrients for the winter and following spring.
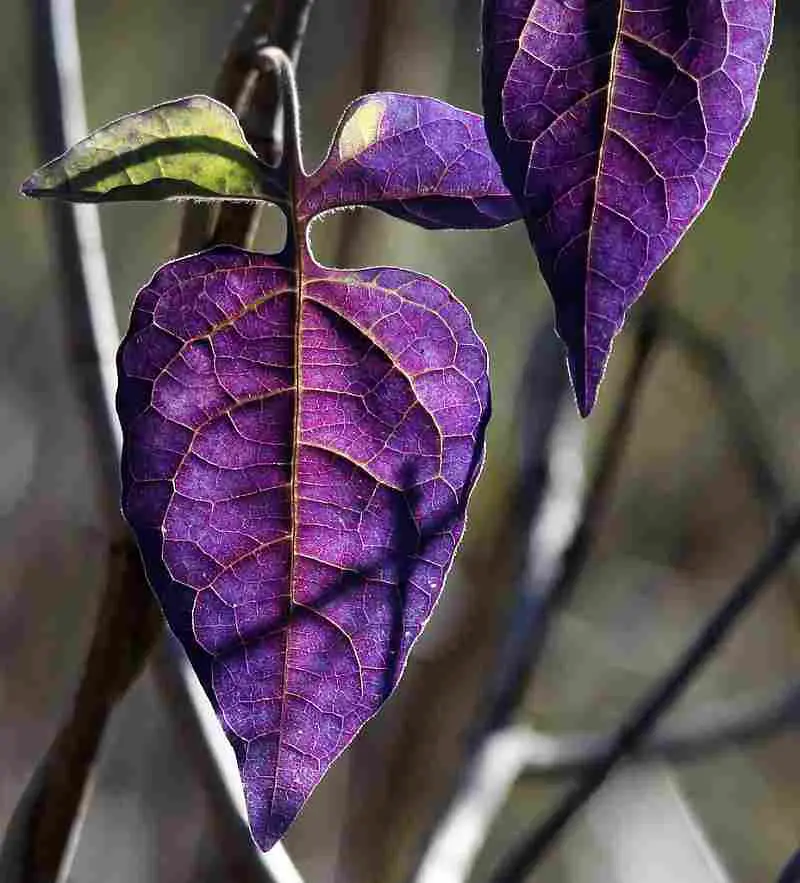
- Trees like Maples, with many sugars inside them, often have exotic reds and purples because of the sugar trapped in the leaves.
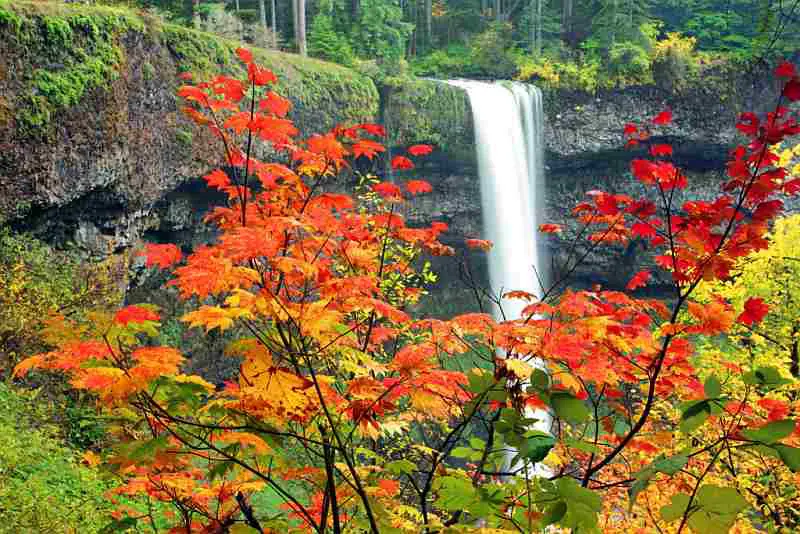
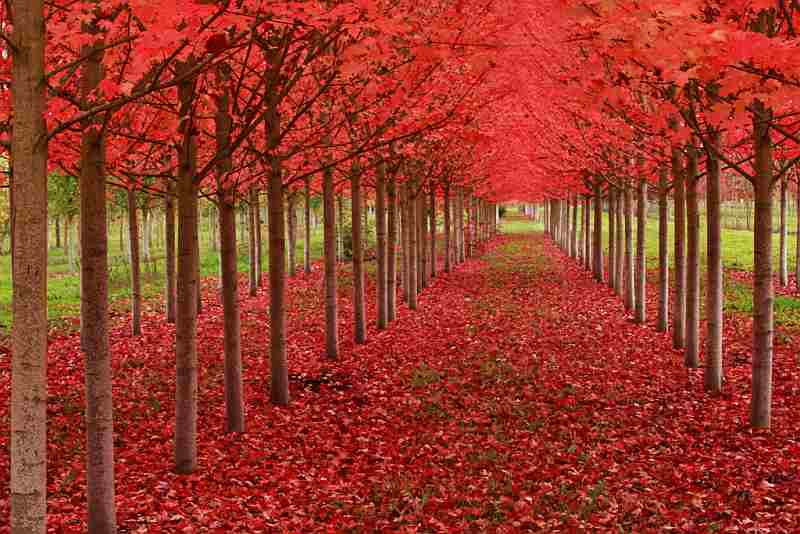
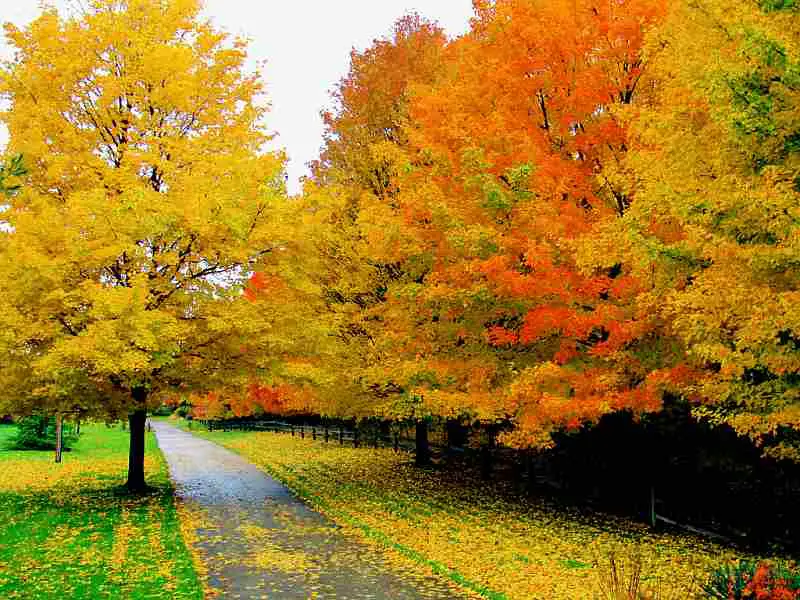
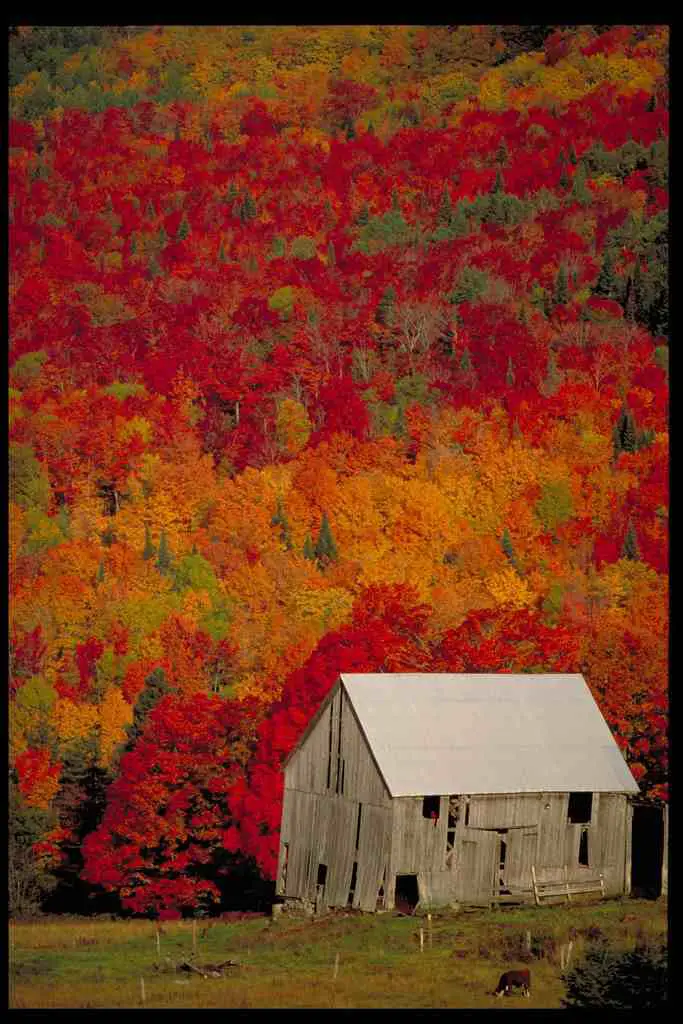
More Great Photos of Fall Foliage Below – Enjoy!